A diagnosis of cancer brings up many important decisions and questions. Typically, your main focus is to explore your treatment options such as radiation, chemotherapy, or surgery. One area that you may not think about, though, is future fertility preservation. Many types of chemotherapy and radiation will save your life but will unfortunately also leave you infertile. For patients who want to have children, this can be devastating. The good news is there are several fertility preservation options for women diagnosed with cancer, and even girls diagnosed with cancer, are available. Ideally fertility preservation should be pursued before the initiation of cancer treatment, but in some cases it is possible to do fertility preservation during or after cancer treatment.
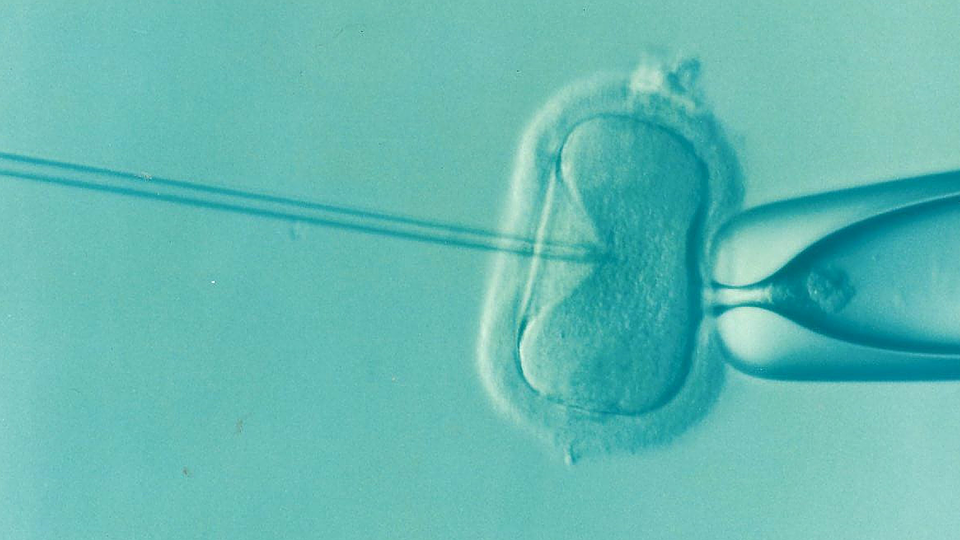
IVF / Embryo Freezing
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a procedure in which a physician will use hormones to stimulate the development of several eggs that can be removed from the ovaries that are then fertilized by the sperm of a partner or donor inside the embryology laboratory. The embryos are then frozen until pregnancy is desired. When a couple decides to start their family, the embryos are placed back into the woman’s uterus. IVF, which has become mainstream and widely accepted in recent years, is the most successful fertility preservation treatment available using your own eggs and sperm (or donor sperm).
Egg Freezing
Egg Freezing (oocyte cryopreservation) is a procedure where a woman’s eggs (oocytes) are retrieved and frozen until pregnancy is desired. Egg freezing is an option prior to cancer treatment if you do not have a partner, do not want to use partner or donor sperm, or do not want to pursue embryo freezing. The process is considered a standard outpatient procedure and takes between two and three weeks. Your eggs will be available when you have completed your cancer treatment and have been cleared to move forward with attempting pregnancy.
Ovarian Tissue Freezing
Ovarian Tissue Freezing, a relatively new and experimental approach to preserving a woman’s fertility, is the only fertility preservation option for young girls who are not old enough to produce mature eggs and cannot pursue embryo freezing or egg freezing. This technique was originally developed to preserve the fertility of young women undergoing cancer chemotherapy and radiation. During this procedure, a woman or child’s ovarian tissue is harvested and frozen, with the ultimate goal of being re-transplanted after cancer treatment to restore hormonal production and fertility. Some day, it may be possible to mature immature follicles in the IVF laboratory.
GnRH Agonist
Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) Agonist treatments are used to cause the ovaries to temporarily shut down, placing patients in a menopausal state during chemotherapy. Ovarian suppression is an experimental technique done through monthly injections, ideally beginning two-four weeks before chemotherapy. This method does not protect against the effects of radiation. It is most commonly used by young breast cancer patients who are at risk for early menopause. The effectiveness of GnRH agonist treatment for fertility preservation is actively debated.
Gonadopexy
Gonadopexy is a procedure which involves surgically moving the ovaries out of the pelvis in women or girls receiving pelvic radiation therapy.
Interested in learning more about preserving your fertility? Contact The Fertility Preservation in Pittsburgh today.